Do you have a piece of jewelry with a missing
diamond or color stone? We have a large selection of loose
diamonds, available in all sizes, shapes and price ranges
including G.I.A. and E.G.L. certified diamonds.
We will help you find the best value for
the size and quality diamond you are looking for. Let us replace the missing
stone today!


| How
Diamonds are
Graded and
Valued |
| |
|
Information on diamond grades, colors, clarity, shapes &
flawless diamonds. |
Because no two gemstones are
alike, sophisticated grading systems have been developed to
measure a diamond's variable qualities. It is possible for a
diamond expert to classify a single stone into one of 2,000
separate categories. The variable qualities of diamonds are
grouped into four major categories, commonly referred to as the
"Four C's": CARAT, COLOR, CLARITY, and CUT.
As a potential diamond owner,
it is advisable to know what gives your diamond its unique
value.
While minor variations in any
of the following categories may affect the value of your diamond
tremendously, all diamonds are subject to classification
according to these four terms.
1) CUT
- Cut refers to two things: the shape
of the diamond and the proportions of the faceted stone.
Diamonds may be cut in round, oval, marquise, pear shape,
emerald or other exotic shapes. Historically, the round
brilliant cut has been most in demand and has shown the greatest
appreciation. The quality diamond is proportioned with
mathematical precision. Any noticeable deviation from proper
proportions will affect the diamond's brilliance, and hence its
price.
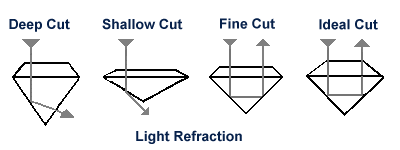
The cut of
a diamond will determine how light is refracted back out and
this will determine the fire and brilliance of the stone. A well
cut diamond refracts nearly all the light entering it out of the
top (crown) and sides. This results in the form of greater fire
and more brilliance.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Round |
Marquise |
Emerald |
Pear |
Princess |
Oval |
Heart |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Asscher |
Triangle |
|
|
Cushion |
Half Moon |
Radiant |
We have all shapes and sizes available!
2) CARAT
WEIGHT -
This adopted measure of weight calls for each carat to be
subdivided into 100 "points" (By comparison, one carat equals
l/5th of one gram, or 1/142 of one ounce.) All other
characteristics being equal, the larger diamond will command the
greater price. Diamonds are weighed with exact precision, using
the metric carat system. While there is no guarantee that
current trends will remain consistent, history dictates a faster
appreciation for larger stones, and the greatest appreciation
for those of the finest quality.
3) COLOR
- Diamonds are graded for color on a
scale of "D" or colorless, to "Z" (Dark Yellow). While diamonds
may be virtually any color, those with "white" or colorless
features are most in demand and greater in value. The
significance of a diamond's color on the stone's price is an
important factor to consider. Just as history shows a higher
appreciation for larger stones, it also shows the greatest
appreciation for those in the higher color categories. Several
grading systems exist, but the most accurate involves use of a
reflectance spectrophotometer. This instrument eliminates
opinion and is able to measure color with plus-or-minus 3
accuracy on a scale of 10.000 units.

|
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
|
Colorless |
Near
Colorless |
Faint
Yellow |
Very Light
Yellow |
|
|
4) CLARITY
- Diamonds are graded according to
their degree of clarity, with the finest referred to as
"flawless": free of inclusions and imperfections when viewed
through 10 x magnification. Diamonds which show very, very
slight imperfections, detected through 10 x magnification, are
designated as "VVS." Diamonds with minor inclusions are assigned
"VS" or "SI" ratings. Finally, those diamonds with visible
inclusions are assigned "Imperfect" ratings.
The
inclusions shown are only visable with a 10X diamond loupe and
cannot be seen with a naked eye above.
|